Chondromalacia Patella – Knee Pain – Patellar Tracking Dysfunction
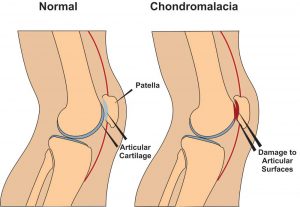 Chondromalacia patella, also known as ”Runners Knee” is one of the most common causes of knee pain in runners. The condition results from irritation of the cartilage on the under-surface of the kneecap. This cartilage is smooth and the kneecap normally glides effortlessly across it during bending of the knee joint. In some individuals however the kneecap does not track so smoothly due to poor alignment and the cartilage surface becomes irritated, resulting in inflammation and knee pain. In more severe cases there can be breakdown of the cartilage. Chondromalacia patella can affect athletes of any age but tends to be more common in women, most likely due to anatomical differences between the sexes ie. wider hips in females which results in a greater angulation between hip and knee, thus resulting in increased lateral forces on the patella.
Chondromalacia patella, also known as ”Runners Knee” is one of the most common causes of knee pain in runners. The condition results from irritation of the cartilage on the under-surface of the kneecap. This cartilage is smooth and the kneecap normally glides effortlessly across it during bending of the knee joint. In some individuals however the kneecap does not track so smoothly due to poor alignment and the cartilage surface becomes irritated, resulting in inflammation and knee pain. In more severe cases there can be breakdown of the cartilage. Chondromalacia patella can affect athletes of any age but tends to be more common in women, most likely due to anatomical differences between the sexes ie. wider hips in females which results in a greater angulation between hip and knee, thus resulting in increased lateral forces on the patella.
Chondromalacia Patella – Causes
There are several causes both structural and dynamic which are linked to the condition. These include excessive foot pronation(feet turn out when running etc.), tight IT band, tight vastus lateralis(basically outer lower quad), weak or slow firing vastus medialis (basically lower inner quad), increased Q angle (simply put the angle between the outer hip and centre of the knee), a lateral femoral condyle that is not sufficiently prominent anteriorly (simply put the knee joint does not fit together properly),and a small or high riding patella(knee cap).(McConnell, 2002)
Chondromalacia Patella – Symptoms
The most common symptom is a dull, aching pain in the front of the knee, behind the kneecap. This pain is often worse when you go up or down stairs. It also can flare up after you have been sitting in one position for a long time. For example, your knee may be painful and stiff when you stand up after watching a movie or after a long trip in a car or plane. In some cases, the painful knee also can appear puffy or swollen. Chondromalacia can sometimes cause a creaky sound or grinding sensation known as ”crepitus” when you move your knee.
Chondromalacia Patella – Physio Treatment
Suitable treatment may involve 1. Soft tissue work to loosen tightened structures such as vastus lateralis muscle, IT band, lateral retinaculum etc., 2.Strengthening of weak structures such as vastus medialis, glutes , hip abductors etc., 3. Correction of overpronation using orthotics, 4. Non steroidal anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen to reduce pain and inflammation, 5. Rest with gradual return to exercise, 6. Taping to correct tracking can be a short term solution.(Hertling and Kessler, 2006) while you strengthen the vastus medialis muscle. Also there are supports you can purchase to help correct patella tracking while exercising. These are a good short term solution while you correct the problems referred to above. Here is a good example.
If nonsurgical treatments fail, or if you have severe symptoms, your doctor may recommend arthroscopy to check the cartilage inside your knee. If the cartilage is softened or shredded, damaged layers can be removed during the surgery, leaving healthy cartilage in place .
References
Hertling, D., Kessler, R.M. ”Management of Common Musculoskeletal Disorders : Physical Therapy Principles and Methods.” Lippincott, Philidelphia 524-533, 2006.
Mc Connell, J. ”The physical therapist’s approach to patellofemoral disorders.” Clinical Sports Medicine 21:363-387, 2002.
For more information on chondromalacia patella see this video.
If you would like to get in touch to discuss your condition or make an appointment for physio in Tralee, please click
here for details.
Regards Eddie.
 cartilage can be damaged by injury or normal wear and tear.
cartilage can be damaged by injury or normal wear and tear.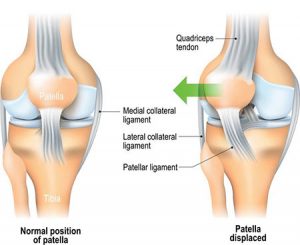 Knee injuries like Chondromalacia patella result from degeneration of cartilage on the underside the kneecap (patella)due to poor alignment of the kneecap (patella) as it slides over the lower end of the thighbone (femur). This condition can also be referred to as patellofemoral syndrome. It usually presents as pain in the front of the knee aggravated by activities such as running, jumping, climbing or descending stairs etc., or by prolonged sitting with knees in a moderately bent position. Patients with chondromalacia patella frequently have abnormal patellar “tracking” toward the lateral (outer) side of the femur. Some patients may also have a vague sense of “tightness” or “fullness” in the knee area with the condition. Mild swelling of the knee area may also occur.
Knee injuries like Chondromalacia patella result from degeneration of cartilage on the underside the kneecap (patella)due to poor alignment of the kneecap (patella) as it slides over the lower end of the thighbone (femur). This condition can also be referred to as patellofemoral syndrome. It usually presents as pain in the front of the knee aggravated by activities such as running, jumping, climbing or descending stairs etc., or by prolonged sitting with knees in a moderately bent position. Patients with chondromalacia patella frequently have abnormal patellar “tracking” toward the lateral (outer) side of the femur. Some patients may also have a vague sense of “tightness” or “fullness” in the knee area with the condition. Mild swelling of the knee area may also occur.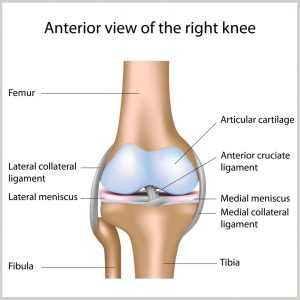 Any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, especially when putting your full weight on it, can lead to a torn meniscus. Each of your knees has two menisci — C-shaped pieces of cartilage that act like a cushion between your shinbone and your thighbone. A torn meniscus causes pain, swelling and stiffness. You might also feel your knee lock and have trouble extending it fully. Conservative treatment — such as rest, ice and medication — is sometimes enough to relieve the pain of a torn meniscus and allow the injury time to settle down on its own. In other cases, however, a torn meniscus requires surgical repair.
Any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, especially when putting your full weight on it, can lead to a torn meniscus. Each of your knees has two menisci — C-shaped pieces of cartilage that act like a cushion between your shinbone and your thighbone. A torn meniscus causes pain, swelling and stiffness. You might also feel your knee lock and have trouble extending it fully. Conservative treatment — such as rest, ice and medication — is sometimes enough to relieve the pain of a torn meniscus and allow the injury time to settle down on its own. In other cases, however, a torn meniscus requires surgical repair.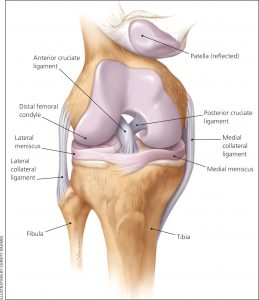 These ligaments are found inside your knee joint. They cross each other to form an “X” with the anterior cruciate ligament in front and the posterior cruciate ligament in back. The cruciate ligaments stabilize the knee. About half of all injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament occur along with damage to other structures of the knee, such as articular cartilage, meniscus, or other ligaments. Partial tears of the anterior cruciate ligament are rare; most ACL injuries are complete or near complete tears.
These ligaments are found inside your knee joint. They cross each other to form an “X” with the anterior cruciate ligament in front and the posterior cruciate ligament in back. The cruciate ligaments stabilize the knee. About half of all injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament occur along with damage to other structures of the knee, such as articular cartilage, meniscus, or other ligaments. Partial tears of the anterior cruciate ligament are rare; most ACL injuries are complete or near complete tears.
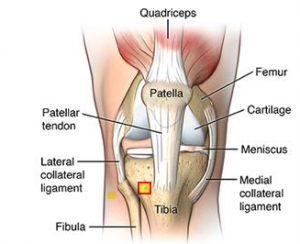 Patellar tendinopathy(also known as Jumper’s knee) is an overuse injury affecting this knee tendon. There are a number of factors which can contribute to the development of patellar tendinopathies. These include:
Patellar tendinopathy(also known as Jumper’s knee) is an overuse injury affecting this knee tendon. There are a number of factors which can contribute to the development of patellar tendinopathies. These include: Osgood-Schlatter disease is a common cause of knee pain in growing adolescents. It is an inflammation of the area just below the knee where the tendon from the kneecap (patellar tendon) attaches to the shinbone (tibia) called the tibial tuberosity. The condition gets worse with activity and better with rest. Osgood-Schlatter disease most often occurs during growth spurts, when bones, muscles, tendons, and other structures are changing rapidly. Because physical activity puts additional stress on bones and muscles, children who participate in athletics — especially running and jumping sports – are at an increased risk for this condition. However, less active adolescents may also experience this problem. The condition normally resolves over time but can be anything from a few weeks/months to two years. It is nothing to worry about. A child can remain active but pain from the condition itself will limit that activity. Icing the area of pain and stretching leg muscles especially quads can help. NSAIDs can be used to relief the pain and inflammation but should be used sparingly and under doctors supervision.
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a common cause of knee pain in growing adolescents. It is an inflammation of the area just below the knee where the tendon from the kneecap (patellar tendon) attaches to the shinbone (tibia) called the tibial tuberosity. The condition gets worse with activity and better with rest. Osgood-Schlatter disease most often occurs during growth spurts, when bones, muscles, tendons, and other structures are changing rapidly. Because physical activity puts additional stress on bones and muscles, children who participate in athletics — especially running and jumping sports – are at an increased risk for this condition. However, less active adolescents may also experience this problem. The condition normally resolves over time but can be anything from a few weeks/months to two years. It is nothing to worry about. A child can remain active but pain from the condition itself will limit that activity. Icing the area of pain and stretching leg muscles especially quads can help. NSAIDs can be used to relief the pain and inflammation but should be used sparingly and under doctors supervision.